Since we are aware of the introduction and basics of the Python language now, hence the next topic about Python is the operators and its different types. First of all, let us understand what is an operator.
What is an Operator?
Operators are the symbols used to perform some operation on one or more than one variables. We use it to perform different operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and many more.
Operators in Python
Following are the types of Operators in Python:
- Arithmetic operator
- Assignment operator
- Relational operator
- Logical operator
- Bitwise operator
- Special operator: This has two types, namely-
- Identity operator
- Membership operator
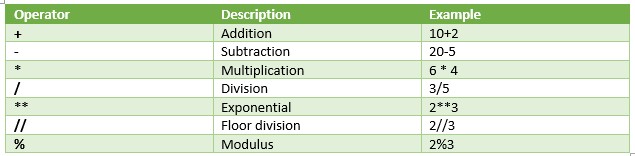
Arithmetic Operator
The first type is the Arithmetic operators. These are used to perform arithmetic operation. As a result, the basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulus, exponential and floor division gets executed using these operators.
These are:
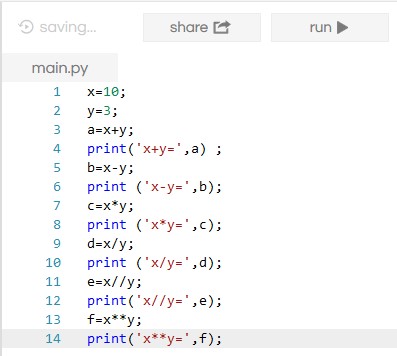
Example:
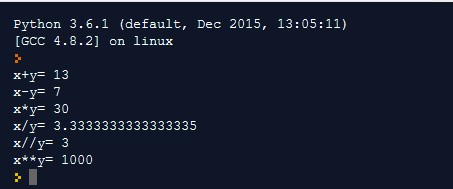
Output:
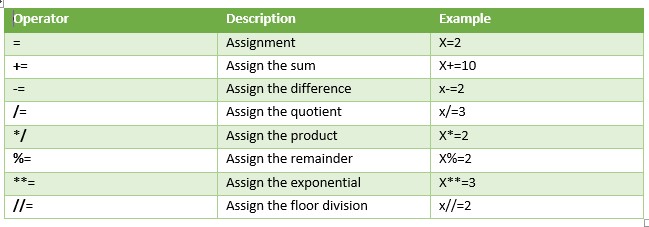
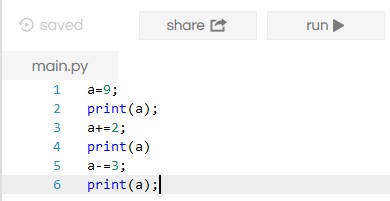
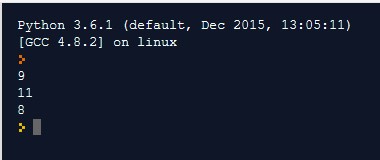
Assignment Operator
It is another category of the Operators. It assigns the value of the right-hand side to the left-hand side of the variable. Hence, a variable is assigned with the desired value for further calculations. The following table shows the list.
Example:
Output:
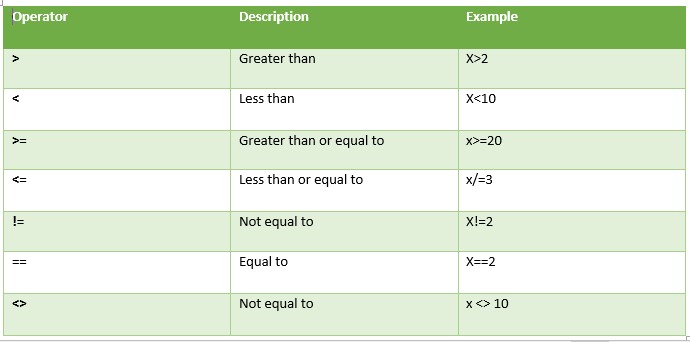
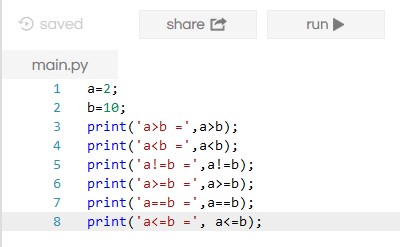
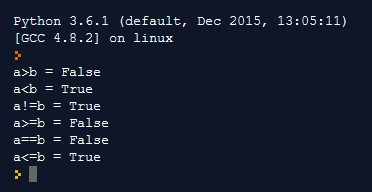
Relational Operator
The relational operator most noteworthy compares two operands. These are –
Example:
Output:
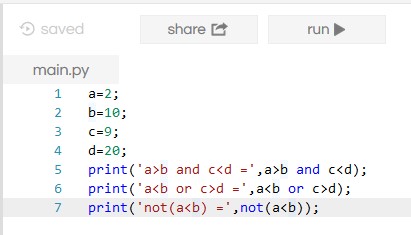
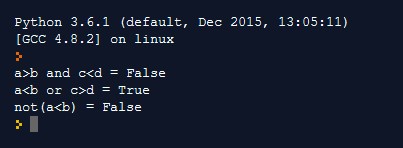
Logical Operator
It combines two or more conditions together. Due to which, it compares the logical condition depending on the operator. The table is given below.
Example:
Output:
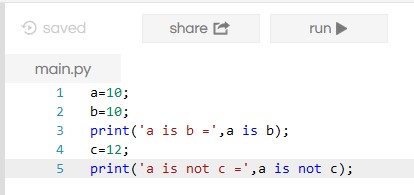
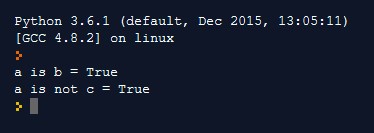
Identify Operator
It checks, if the two operands are present in the same memory location or not. These are :
Example:
Output:
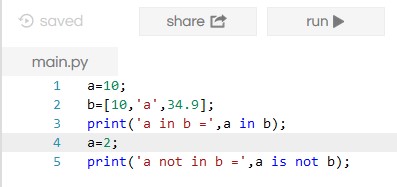
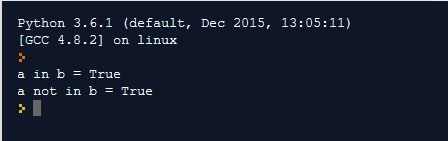
Membership Operator
It tests, whether the value or a variable is in the sequence, i.e., list, string, set, tuple, and dictionary.
Example:
Output:
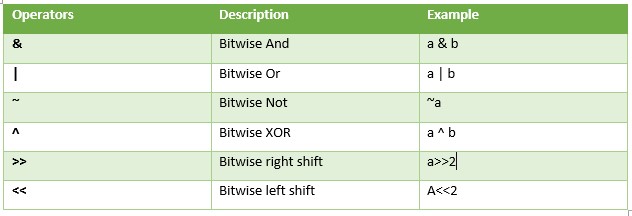
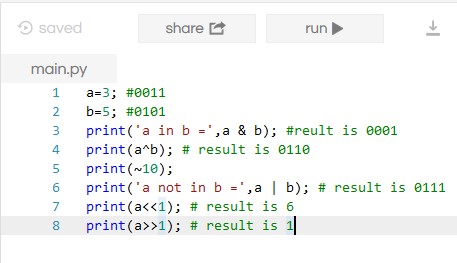
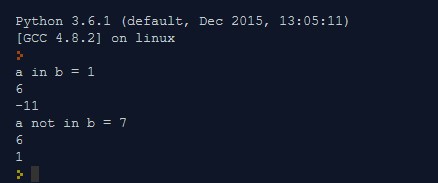
Bitwise Operator
It works on a bit and performs operations bit by bit. Below is the table with description and example.
Example:
Output:








Python is very easy topic
And easy to learn
Python is very easy topic
And easy to learn